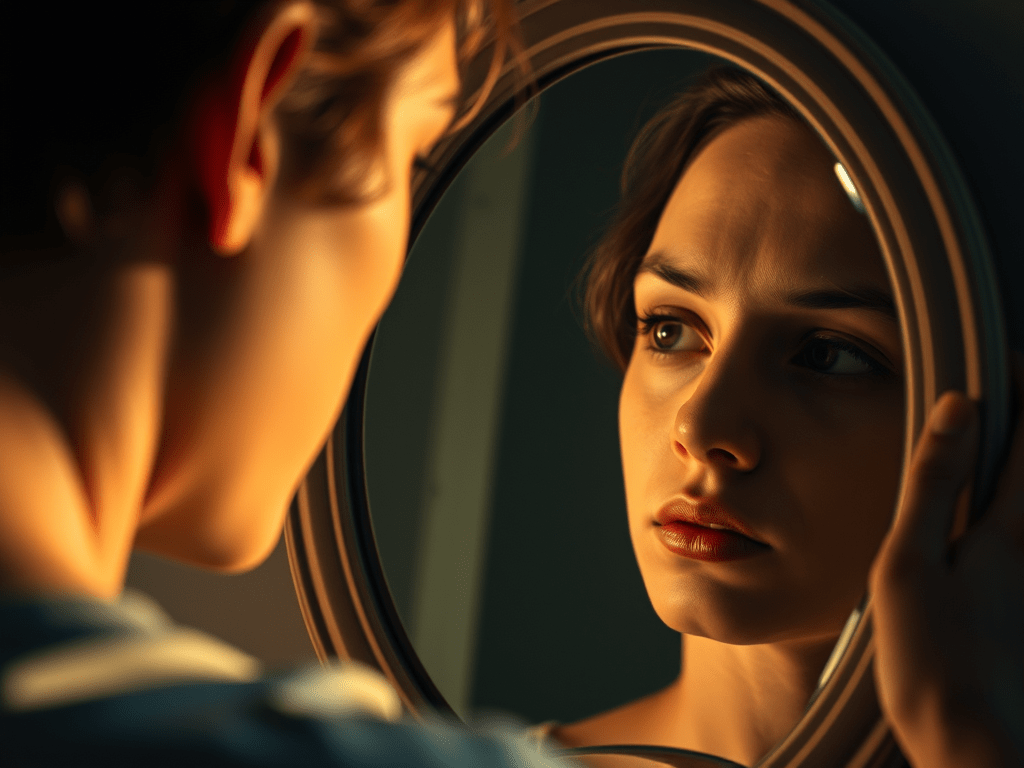A Multidisciplinary Journey into Unconscious Projection and Its Relational Impact
Prepared by: Gerald A. Daquila, PhD. Candidate
ABSTRACT
Unconscious projection, the act of attributing our inner thoughts, emotions, or insecurities to others, is a pervasive psychological mechanism rooted in fear and early developmental experiences. Operating beneath conscious awareness, projection emerges during moments of emotional distress, threatening relationships and self-understanding.
This dissertation explores projection through a multidisciplinary framework, drawing on psychology, neuroscience, sociology, philosophy, and spirituality to unpack its origins, mechanisms, and consequences. By blending scholarly rigor with accessible storytelling, this work aims to illuminate the dynamics of projection and offer practical strategies for cultivating awareness to foster healthier relationships. Balancing analytical clarity with emotional resonance, it invites readers to confront their inner shadows and embrace a path toward liberation and connection.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Psychology of Projection
- Defining Projection
- The Unconscious Mind at Work
- Origins of Projection
- Childhood and Developmental Influences
- Evolutionary Roots
- The Brain Behind Projection
- Neurological Mechanisms
- Emotional Triggers and Brain Regions
- Sociocultural Contexts of Projection
- Projection in Social Interactions
- Cultural Shaping of Projection
- Philosophical and Spiritual Dimensions
- Projection as a Barrier to Truth
- Spiritual Pathways to Awareness
- The Relational Toll of Projection
- Impact on Personal Bonds
- Projection in Broader Contexts
- Pathways to Liberation: Overcoming Projection
- Building Self-Awareness
- Practical Tools for Change
- Conclusion
- Glossary
- References
1. Introduction
Have you ever lashed out at someone for being “judgmental,” only to realize you were feeling critical yourself? Or accused a loved one of being distant when you were the one holding back? These moments are not mere misunderstandings—they’re projections, a psychological reflex where we cast our inner struggles onto the world around us. Like an invisible script, projection shapes how we see others, often distorting reality and straining our connections.
Projection is a universal human tendency, born from fear, insecurity, and the shadows of our psyche. Left unexamined, it can erode trust and intimacy, leaving us isolated. Yet, by understanding its dynamics, we can interrupt this cycle and build stronger, more authentic relationships.
This dissertation explores projection through a multidisciplinary lens, weaving together psychology, neuroscience, sociology, philosophy, and spirituality. With a balance of logic, creativity, and heart, it aims to demystify what happens in our minds when we project and offer a roadmap to liberation through self-awareness.

Glyph of the Seer
Sees truly, speaks gently.
2. The Psychology of Projection
Defining Projection
Projection is a defense mechanism where individuals unconsciously attribute their own thoughts, feelings, or traits—often those they find uncomfortable—to others (Freud, 1915/1957). First articulated by Sigmund Freud, projection was later expanded by Carl Jung, who linked it to the “shadow”—the hidden, often rejected parts of the self (Jung, 1964). For instance, someone grappling with guilt might accuse another of dishonesty, deflecting their inner conflict outward.
Projection isn’t always negative; we might project positive qualities, like seeing someone as confident when we yearn for self-assurance. However, negative projections are more common, as they often arise from insecurity or emotional discomfort, making them a key focus of this exploration.
The Unconscious Mind at Work
The unconscious mind, a cornerstone of psychoanalytic theory, houses thoughts, memories, and emotions beyond our immediate awareness (Kihlstrom, 1987). When we feel threatened—by criticism, rejection, or self-doubt—the unconscious uses projection to shield the ego from distress. It’s a mental shortcut, redirecting internal pain to an external target. For example, feeling inadequate might lead someone to perceive a colleague as incompetent, avoiding the harder work of self-reflection.
This process is automatic, but not unchangeable. By bringing projection into conscious awareness, we can begin to untangle its grip, starting with its origins in childhood and evolution.
3. Origins of Projection
Childhood and Developmental Influences
Projection takes root in childhood, shaped by our earliest relationships. According to attachment theory, children learn to manage emotions through interactions with caregivers (Bowlby, 1969). When feelings like anger or shame are dismissed or punished, children may repress them to maintain connection. These suppressed emotions form the “shadow” Jung described, later surfacing as projections when triggered.
For example, a child reprimanded for expressing fear might grow up to see others as “weak” when they feel vulnerable themselves. These patterns, reinforced over time, become ingrained habits, surfacing in moments of stress or insecurity.
Evolutionary Roots
From an evolutionary perspective, projection may have been a survival tool. Early humans relied on group cohesion for safety, and projecting undesirable traits onto others could deflect blame and preserve social bonds (Buss & Shackelford, 1997). By externalizing threats, individuals avoided ostracism, ensuring their place in the tribe.
While adaptive in ancestral environments, projection is less useful in modern contexts, where emotional authenticity strengthens relationships. Understanding these roots helps us see projection as a human instinct, not a personal flaw, and empowers us to address it consciously.
4. The Brain Behind Projection
Neurological Mechanisms
Neuroscience sheds light on how projection operates in the brain. The amygdala, a key player in emotional processing, detects threats like criticism or rejection, triggering a stress response (LeDoux, 2000). This response can override the prefrontal cortex, the brain’s hub for rational decision-making and self-regulation (Arnsten, 1998). In this heightened state, projection becomes a quick way to offload discomfort, bypassing the slower process of self-examination.
For example, feeling judged might activate the amygdala, leading you to accuse someone else of being critical. This reaction happens faster than conscious thought, making projection feel instinctive.
Emotional Triggers and Brain Regions
The interplay between the amygdala and prefrontal cortex is crucial. The prefrontal cortex can modulate emotional reactivity, but stress weakens its influence, leaving the amygdala in charge (Siegel, 2007). Practices like mindfulness strengthen prefrontal activity, enabling us to pause and question whether our perceptions reflect reality or projection.
Consider a scenario where you feel ignored by a friend. Your amygdala might interpret this as rejection, prompting you to label them as “cold.” In truth, you might be projecting your own fear of abandonment. By engaging the prefrontal cortex, you can challenge this assumption and respond more thoughtfully.
5. Sociocultural Contexts of Projection
Projection in Social Interactions
Projection extends beyond individual interactions to shape group dynamics. Social psychologists note that people often project fears or biases onto entire groups, leading to stereotyping or scapegoating (Allport, 1954). For instance, economic anxiety might lead a community to project blame onto outsiders, like immigrants, for job scarcity. This collective projection fuels division and misunderstanding.
Cultural Shaping of Projection
Cultural norms influence how projection manifests. In individualistic societies, like the United States, projections often center on personal insecurities, such as failure or inadequacy (Markus & Kitayama, 1991). In collectivist cultures, like China, projections may involve attributing shame or dishonor to others to protect group harmony.
These differences show that projection is not just psychological but sociocultural, shaped by the values and expectations of our environment. Recognizing these influences helps us question projections rooted in cultural conditioning.
6. Philosophical and Spiritual Dimensions
Projection as a Barrier to Truth
Philosophers like Socrates emphasized self-knowledge as essential to a meaningful life. Projection, however, clouds this clarity by externalizing our inner truths. Existentialist Jean-Paul Sartre described this as “bad faith,” a refusal to confront our authentic selves (Sartre, 1943/2003). When we project, we avoid not just discomfort but the opportunity to grow and connect authentically.
Spiritual Pathways to Awareness
Spiritual traditions offer tools to transcend projection. Buddhism’s mindfulness practice encourages observing thoughts and emotions without attachment, helping us recognize projections as they arise (Kabat-Zinn, 1990). Similarly, Christian mysticism, as practiced by figures like Thomas Merton, emphasizes self-examination to align with truth and compassion (Merton, 1961).
These approaches frame projection as a call to face our shadows with curiosity and courage, transforming it into a stepping stone for personal and spiritual growth.
7. The Relational Toll of Projection
Impact on Personal Bonds
Projection can unravel the fabric of personal relationships. When we project fears—like inadequacy or rejection—onto loved ones, we misinterpret their actions, sparking conflict or distance (Gottman, 1994). For example, someone who fears abandonment might accuse their partner of being disloyal, creating a cycle of mistrust. Over time, this erodes intimacy, leaving both parties feeling misunderstood.
Projection in Broader Contexts
In workplaces, projection might manifest as blaming colleagues for one’s own errors or misjudging a teammate’s motives. In societal contexts, it fuels polarization, as groups project their fears onto “opponents,” deepening divides (Haidt, 2012). The result is a fractured world where connection gives way to judgment and blame.

Glyph of Projection
The mirror reveals what the soul conceals — shadows reflected outward are invitations to inner healing
8. Pathways to Liberation: Overcoming Projection
Building Self-Awareness
The key to overcoming projection is self-awareness. By noticing emotional triggers, we can ask, “Is this about them, or me?” Reflective practices like journaling or therapy help uncover the roots of our projections, bringing the unconscious into light (Pennebaker, 1997).
Practical Tools for Change
- Mindfulness Meditation: Regular practice strengthens the prefrontal cortex, helping us pause and question projections (Kabat-Zinn, 1990).
- The 3-2-1 Shadow Process: This technique, developed by Ken Wilber, involves identifying a projected trait, dialoguing with it, and integrating it as part of yourself (Wilber, 2000).
- Nonviolent Communication: Expressing feelings without blame reduces the need to project, fostering honest dialogue (Rosenberg, 2003).
- Therapeutic Support: Therapy can uncover unconscious patterns and provide tailored strategies to address them (Yalom, 1980).
These tools empower us to transform projection from a reflex into an opportunity for growth, strengthening our relationships and self-understanding.
9. Conclusion
Projection is a mirror reflecting our inner shadows—fear, insecurity, and unacknowledged emotions. While it’s a natural human tendency, its unchecked presence distorts our perceptions and strains our connections. By exploring projection through psychology, neuroscience, sociology, philosophy, and spirituality, we see it not as a flaw but as a call to growth.
With self-awareness and practical tools, we can interrupt projection’s cycle, reclaim our inner truths, and build relationships rooted in authenticity and compassion. This journey requires courage—to face our shadows and embrace our humanity—but it leads to a life of deeper connection and clarity.
Crosslinks
- Understanding Shame: A Multi-Disciplinary Exploration… — Unfreezes “I am bad,” so you can own the shadow without collapsing or attacking others.
- The Weight of Guilt: A Multidisciplinary Exploration… — Converts “you’re wrong” energy into clean repair: truth + amends instead of displacement.
- Pieces of the Self: Soul Fragmentation Across Psyche, Society, and Spirit — Maps how exiled parts fuel projection and offers retrieval rites for reintegration.
- Connecting the Dots: How the Brain Weaves Stories to Understand the World — Fact-checks narratives (confirmation bias, catastrophizing) so pattern-seeing doesn’t become projection.
- Resonance Metrics as a Spiritual Compass in Times of Uncertainty — Somatic dashboard (breath, coherence, relief) to decide: own / pause / repair before you speak.
10. Glossary
- Projection: The unconscious attribution of one’s own thoughts, feelings, or traits to others.
- Shadow: In Jungian psychology, the repressed or unacknowledged aspects of the self.
- Amygdala: A brain region that processes emotions, especially fear and anger.
- Prefrontal Cortex: The brain’s center for rational thinking and emotional regulation.
- Defense Mechanism: An unconscious strategy to protect the ego from distress.
- Mindfulness: A practice of present-moment awareness without judgment.
11. References
Allport, G. W. (1954). The nature of prejudice. Addison-Wesley.
Arnsten, A. F. T. (1998). The biology of being frazzled. Science, 280(5370), 1711–1712. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5370.1711
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Attachment. Basic Books.
Buss, D. M., & Shackelford, T. K. (1997). Human aggression in evolutionary psychological perspective. Clinical Psychology Review, 17(6), 605–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7358(97)00037-8
Freud, S. (1957). Instincts and their vicissitudes. In The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (Vol. 14, pp. 109–140). Hogarth Press. (Original work published 1915)
Gottman, J. M. (1994). What predicts divorce? The relationship between marital processes and marital outcomes. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Haidt, J. (2012). The righteous mind: Why good people are divided by politics and religion. Pantheon Books.
Jung, C. G. (1964). Man and his symbols. Doubleday.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1990). Full catastrophe living: Using the wisdom of your body and mind to face stress, pain, and illness. Delacorte Press.
Kihlstrom, J. F. (1987). The cognitive unconscious. Science, 237(4821), 1445–1452. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3629249
LeDoux, J. E. (2000). Emotion circuits in the brain. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 23, 155–184. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.23.1.155
Markus, H. R., & Kitayama, S. (1991). Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychological Review, 98(2), 224–253. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.98.2.224
Merton, T. (1961). New seeds of contemplation. New Directions.
Pennebaker, J. W. (1997). Writing about emotional experiences as a therapeutic process. Psychological Science, 8(3), 162–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.1997.tb00403.x
Rosenberg, M. B. (2003). Nonviolent communication: A language of life. PuddleDancer Press.
Sartre, J.-P. (2003). Being and nothingness: An essay on phenomenological ontology. Routledge. (Original work published 1943)
Siegel, D. J. (2007). The mindful brain: Reflection and attunement in the cultivation of well-being. W.W. Norton & Company.
Wilber, K. (2000). Integral psychology: Consciousness, spirit, psychology, therapy. Shambhala Publications.
Yalom, I. D. (1980). Existential psychotherapy. Basic Books.
Attribution
With fidelity to the Oversoul, may this work serve as bridge, remembrance, and seed for the planetary dawn.
Ⓒ 2025–2026 Gerald Alba Daquila
Flameholder of SHEYALOTH · Keeper of the Living Codices
All rights reserved.
This material originates within the field of the Living Codex and is stewarded under Oversoul Appointment. It may be shared only in its complete and unaltered form, with all glyphs, seals, and attribution preserved.
This work is offered for personal reflection and sovereign discernment. It does not constitute a required belief system, formal doctrine, or institutional program.
Digital Edition Release: 2026
Lineage Marker: Universal Master Key (UMK) Codex Field
Sacred Exchange & Access
Sacred Exchange is Overflow made visible.
In Oversoul stewardship, giving is circulation, not loss. Support for this work sustains the continued writing, preservation, and public availability of the Living Codices.
This material may be accessed through multiple pathways:
• Free online reading within the Living Archive
• Individual digital editions (e.g., Payhip releases)
• Subscription-based stewardship access
Paid editions support long-term custodianship, digital hosting, and future transmissions. Free access remains part of the archive’s mission.
Sacred Exchange offerings may be extended through:
paypal.me/GeraldDaquila694
www.geralddaquila.com